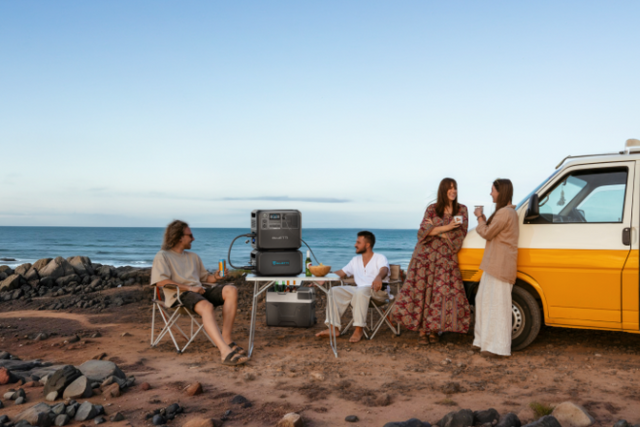
November marks the beginning of summer in Australia, and as temperatures rise, many households start relying on fans to stay cool. Whether it's ceiling fans or portable ones, understanding their electricity consumption is crucial for optimizing energy use at home. In this article, we'll delve into the power usage of different types of fans, helping you make informed choices to enjoy a refreshing environment while keeping your electricity bills in check.
As November ushers in the Australian summer, staying cool becomes a top priority. Whether you’re in a cozy apartment or off camping under the stars, choosing the right fan can make all the difference.
Typical Wattage Ranges for Different Types of Fans
| Fan Type | Wattage Range | Power Consumption | Suitable Settings | User Capacity | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceiling Fan | 10-120 Watts | 0.01-0.12 kWh/hr | Home (Living Rooms, Bedrooms) | Up to 5 | High airflow, may be noisy at higher speeds. |
| Table Fan | 20-60 Watts | 0.02-0.06 kWh/hr | Home, Office | 1-2 | Compact, portable, and usually quieter. |
| Floor Fan | 50-100 Watts | 0.05-0.1 kWh/hr | Home, Outdoor Events | 1-4 | Powerful airflow, may take up more space. |
| Oscillating Fan | 30-80 Watts | 0.03-0.08 kWh/hr | Home, Camping | 1-3 | Provides wider coverage; some models are quiet. |
| Exhaust Fan | 30-75 Watts | 0.03-0.075 kWh/hr | Home (Kitchens, Bathrooms) | 1-2 | Removes stale air; typically quiet operation. |
| Portable Fan | 5-25 Watts | 0.005-0.025 kWh/hr | Camping, Travel | 1-2 | Lightweight, battery-operated options available. |
For true comfort in the sweltering heat, ceiling fans deliver powerful airflow, effortlessly cooling larger spaces. They range from 10 to 120 watts, though be mindful—at high speeds, they can be a bit noisy, making them less than ideal for a peaceful night’s sleep.

Need something more personal? Table fans, consuming just 20 to 60 watts, are your go-to for cozy nooks. They’re compact and portable, designed to fit seamlessly into your workspace or bedroom, and their quieter operation makes them perfect for evening use.
If you’re hosting a gathering or enjoying an outdoor barbecue, floor fans pack a punch with their 50 to 100 watts of power. They provide a robust airflow, ensuring everyone stays cool, though they do require a bit of floor space.
Oscillating fans offer the best of both worlds—efficient cooling with a wider coverage area. Operating between 30 and 80 watts, they’re versatile enough for indoor use or camping trips, with some models designed for whisper-quiet operation.
For those looking to enhance air quality, exhaust fans work diligently at 30 to 75 watts, efficiently removing stale air from kitchens and bathrooms while maintaining a low noise profile.
And for the adventurers, portable fans, with their lightweight design and 5 to 25 watts of consumption, are perfect companions for camping or travel. Some even come with battery options, ensuring you stay cool no matter where your journey takes you.
With the right fan, you can embrace the summer heat, enjoying comfort and energy efficiency without breaking the bank. Whether at home or on the go, there’s a fan tailored to your needs.
What Factors Influence a Fan's Energy Consumption?
When it comes to staying cool during the hot summer months, many of us rely on fans to circulate air and provide some relief from the heat. However, have you ever wondered how much electricity a fan uses? The answer depends on a variety of factors, including the fan's size and type, as well as the duration and frequency of use.
Fan Size and Type
The size and type of fan you have can greatly impact its energy consumption. For example, a small personal fan that sits on your desk or nightstand will likely use much less electricity than a large ceiling fan. This is because smaller fans have smaller blades and require less power to rotate them and circulate air. Additionally, the type of fan can also play a role. Ceiling fans, for instance, have a larger motor and typically use more electricity than pedestal or tower fans.
Duration and Frequency of Use
Another factor that influences a fan's energy consumption is the duration and frequency of use. If you only use your fan for a few hours a day, it will use less electricity compared to someone who runs their fan all day long. Additionally, if you use your fan every day, it will consume more energy than if you only use it a few times a week. It's also essential to consider the time of day you are using your fan. During peak hours when electricity rates are higher, your fan will use more energy.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency
When it comes to choosing a fan, considering its energy efficiency can also greatly impact its electricity usage. Look for fans that have an energy-efficient rating, such as ENERGY STAR. These fans are designed to use less energy while still providing the same airflow and cooling effect. Additionally, some fans come with features like adjustable speed settings and timers, allowing you to control the fan's energy usage and potentially save on your electricity bill.
Tips to Reduce Energy Consumption of a Fan
While fans are a great way to stay cool and save energy compared to air conditioning, there are a few tips you can follow to reduce their energy consumption even further:
- Choose the right size fan for your space to avoid wasting energy on oversized fans.
- Use the fan in conjunction with your air conditioning to help circulate cool air more efficiently.
- Clean and maintain your fan regularly, as a dirty fan will have to work harder and use more energy to circulate air.
- Consider investing in a fan with energy-saving features, such as a timer or speed settings.
the amount of electricity a fan uses depends on various factors, including its size and type, as well as its duration and frequency of use. By choosing an energy-efficient fan and following these tips, you can reduce your fan's energy consumption and save on your electricity bill.

How Can You Calculate the Monthly Energy Consumption of Your Fan?
Calculating the monthly energy consumption of your fan is straightforward and can help you manage your electricity costs effectively. Ready to take control? Let’s dive in.First, determine the wattage of your fan, which you can usually find on the label or in the manual. Let’s say you have a ceiling fan that uses 75 watts. Next, calculate the daily usage: how many hours do you run it each day? If you run it for 6 hours daily, that’s 75 watts x 6 hours = 450 watt-hours (Wh) per day.
To get the monthly consumption, multiply your daily usage by the number of days in a month. So, 450 Wh x 30 days gives you 13,500 Wh, or 13.5 kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Now, to find out how much this costs you, check your electricity rate. If you pay 30 cents per kWh, simply multiply 13.5 kWh by 0.30, resulting in a monthly cost of about $4.05.
By following this simple formula—wattage x hours per day x days per month—you can keep tabs on how much your fan contributes to your energy bill. Want to optimize your savings? Consider using your fan during off-peak hours or pairing it with natural ventilation to minimize usage. With these tips, you’ll stay cool without overheating your budget.

How Does Fan Speed Impact Electricity Usage?
Ceiling fans are a popular and energy-efficient solution for cooling rooms, especially during the scorching summer months. However, many people underestimate the electricity consumption of their fans and how speed settings affect that usage. Let’s explore the connection between fan speed and electricity consumption while offering energy-saving tips for optimal performance.
The Relationship Between Speed Settings and Wattage Consumption
The speed setting of a fan has a direct impact on its electricity consumption. Higher speed settings require more energy because the fan must exert more force to move air effectively. Conversely, lower speed settings use less electricity as the fan exerts less force and moves less air.
For example, a ceiling fan on high speed can consume around 70 to 120 watts, while the low speed fan may only use about 10 to 30 watts, depending on the model. Running a ceiling fan on high speed for 12 hours a day can add approximately 8.4 kilowatt-hours (kWh) to your monthly electricity bill, compared to just 1.2 kWh on low speed. While these numbers may seem modest, they can accumulate over time, resulting in a noticeable impact on your energy costs.
Energy-Saving Tips for Optimal Speed Settings
To conserve energy and lower your electricity bill, it’s essential to operate your ceiling fan at the optimal speed setting. This varies based on room temperature, size, and personal comfort. Generally, it's best to use the lowest speed that still keeps you comfortable.
In warmer climates, high speed may be necessary to create a cooling effect. However, in moderately warm or cool conditions, running the fan on low or medium can provide a pleasant breeze while using significantly less electricity. Always remember to turn off the fan when leaving the room, as operating it without anyone present is simply wasting energy.
Consider using a fan with a built-in timer or installing a separate timer switch. This allows you to set the fan to turn off automatically after a designated period, ensuring it doesn’t run longer than needed. By making these adjustments, you can enjoy the comfort of your fan while keeping your energy bills in check.
For Australian users looking to save on electricity usage with their fans, the BLUETTI AC300+B300K setup offers an ingenious solution.
1. Setup and Operation: Utilize the integrated AC300+B300K system, which cannot be separated, to maximize efficiency. By operating in Time Control UPS Mode, you can charge the system during off-peak hours, storing cheaper electricity for use during peak times. This strategy takes advantage of lower tariffs and reduces overall power expenses.
2. Solar Integration: Enhance efficiency with flexible solar panels. Install these panels in sunlight-rich areas to capture and convert solar energy throughout the day. These panels work seamlessly with the AC300+B300K, feeding renewable energy directly into the system.
3. Powering Fans: Use the AC300+B300K system to run your fans, drawing from stored solar and off-peak energy. This setup is especially suitable for cooling needs during hot Australian afternoons or creating a comfortable environment in shaded outdoor spaces.
4. Sustainable Savings: This method not only cuts down on electricity costs but also promotes an eco-friendly lifestyle, making it a perfect fit for the sunny Australian climate while offering a reliable and resourceful way to stay cool without over-relying on the grid.
Shop products from this article
Be the First to Know
You May Also Like

Save on energy costs by subscribing to the cheapest gas provider in Australia. Find out ways to switch your gas company. Get expert tips on lowering your gas bill.

Discover the latest solar battery prices in Australia for 2025, including ranges and rebates, in a friendly guide.

The Ausnet power outage incidents in 2025, with the official ausnet power outage map, alerts and how you can prepare for pre planned outages easily.